Types of Random Variables
Random Variables can be classified into various categories, based on the nature of the values that a random variable can take. The classification fo the random variables can be presented as a graph below
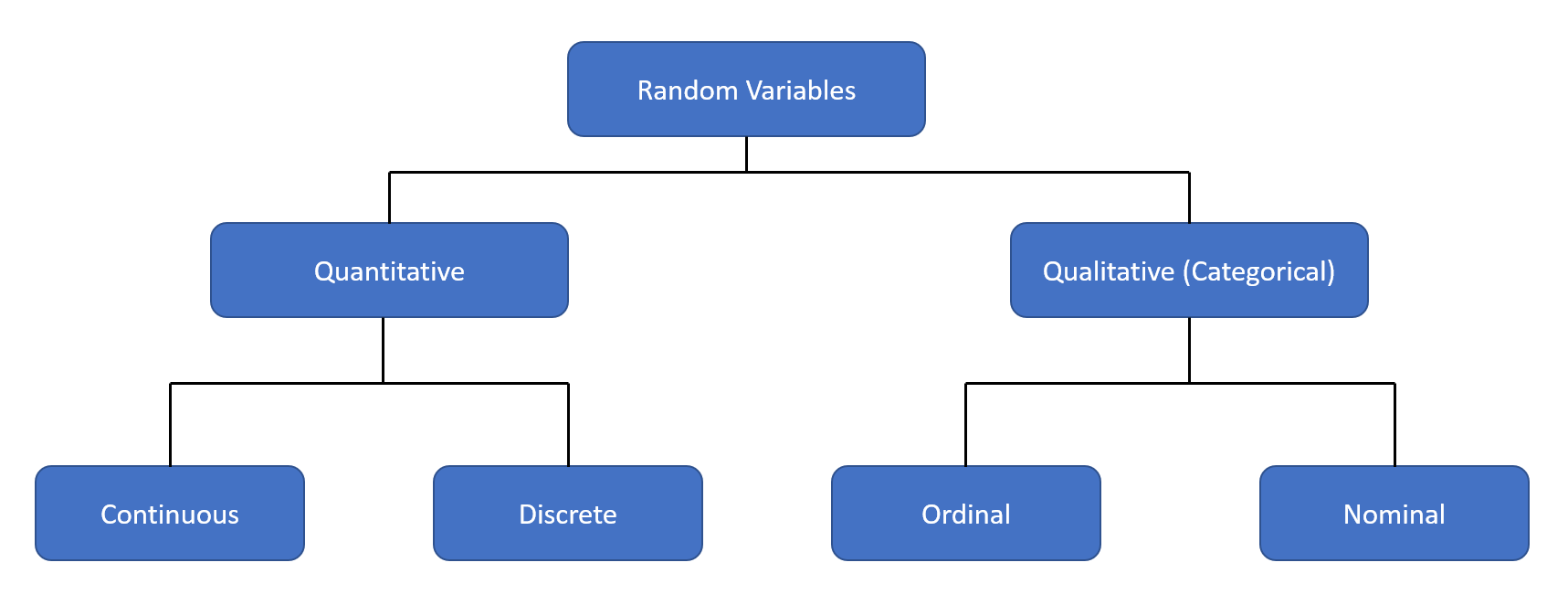
Quantitative Random Variables
The outcome of a random experiment that can be measured as a numerical value is called a quantitative random variable.
Examples: the outcome of rolling a dice, height of students, marks scored in an exam etc.
Continuous Random Variable: The random variable that can be measured as a rational/decimal number are continuous random variables. For example, the height of a student, marks in an exam, etc.
Discrete Random Variable: The random variable that can be measured as an integer number are discrete random variables. For example, the number of calls received in a day, the outcome of rolling a dice, etc.
Qualitative Random Variables
The outcome of a random experiment that can not be measured as a numerical value, but can be classified into categories is called a qualitative or categorical variable.
Examples: Outcome of tossing a coin, blood group of a person, severity of an accident, etc.
Ordinal Random Variable: If the outcomes of random experiments have inherent ordering, then the outcomes of those random experiments are called ordinal random variables. For example, the severity of an accident (fatal, severe, minor, no injuries), grades in an exam (A, B, C, D, F), etc.
Nominal Random Variable: If a random variable is a name or label or category, that does not have order is called a nominal random variable. For example, choice of mode to make a trip (car, bus, bike, etc), destination, etc.